using Random
using Pumas
using PumasUtilities
using CairoMakie
using AlgebraOfGraphics
using DataFramesMeta
using CSV
using Dates
PK41 - Multiple Intravenous Infusions: NCA vs Regression
1 Background
- Structural Model - One compartment model with non-linear elimination.
- Route of administration - IV infusion
- Dosage Regimen - 310 μg, 520 μg, and 780 μg
- Number of Subjects - 3
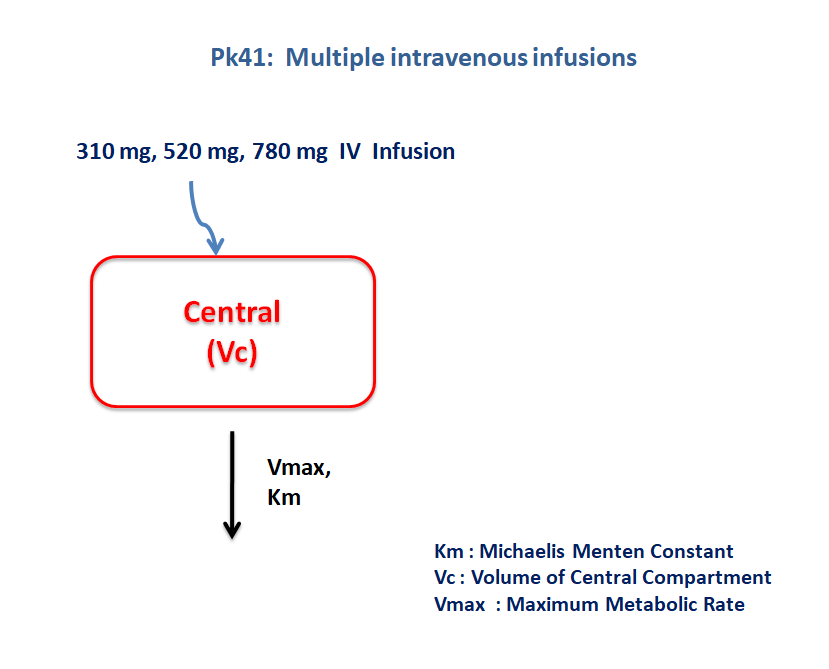
2 Learning Outcome
This is a one compartment model with capacity limited elimination. The concentration time profile was obtained for three subjects administered with three different dosage regimens.
3 Objectives
In this tutorial, you will learn how to build a one compartment model with non-linear elimination.
4 Libraries
Call the necessary libraries to get started.
5 Model
The following model describes the parameters and the differential equation for a one-compartment model with capacity limited elimination
pk_41 = @model begin
@metadata begin
desc = "One Compartment Model"
timeu = u"hr"
end
@param begin
"""
Maximum Metabolic Rate (μg/kg/hr)
"""
tvvmax ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Michaelis Menten Constant (μg/kg/L)
"""
tvkm ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Volume of Central Compartment (L/kg)
"""
tvvc ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
Ω ∈ PDiagDomain(3)
"""
Proportional RUV
"""
σ²_prop ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
end
@random begin
η ~ MvNormal(Ω)
end
@pre begin
Vmax = tvvmax * exp(η[1])
Km = tvkm * exp(η[2])
Vc = tvvc * exp(η[3])
end
@dynamics begin
Central' = -(Vmax * (Central / Vc) / (Km + (Central / Vc)))
end
@vars begin
cp = Central / Vc
end
@derived begin
"""
Observed Concentrations (μg/L)
"""
dv ~ ProportionalNormal.(cp, sqrt(σ²_prop))
end
@observed begin
nca := @nca cp
cl = NCA.cl(nca)
end
endPumasModel
Parameters: tvvmax, tvkm, tvvc, Ω, σ²_prop
Random effects: η
Covariates:
Dynamical system variables: Central
Dynamical system type: Nonlinear ODE
Derived: dv, cp
Observed: cl, dv, cp6 Parameters
The parameters are as given below. Note that tv represents the typical value for parameters.
Vmax- Maximum Metabolic Rate (μg/kg/hr)Km- Michaelis Menten Constant (μg/kg/L)Vc- Volume of Central compartment (L/kg)
param = (
tvvmax = 180.311,
tvkm = 79.8382,
tvvc = 1.80036,
Ω = Diagonal([0.04, 0.04, 0.04]),
σ²_prop = 0.015,
)7 Dosage Regimen
All subjects receive an IV infusion over 5 hours with the following doses:
- Subject 1 receives a dose of 310 μg
- Subject 2 receives a dose of 520 μg
- Subject 3 receives a dose of 780 μg
dose = [310, 520, 780]rate_ind = [62, 104, 156]ids = ["310 μg.kg-1", "520 μg.kg-1", "780 μg.kg-1"]ev(dose, rate) = DosageRegimen(dose; cmt = 1, time = 0, rate, route = NCA.IVInfusion)ev (generic function with 1 method)pop3_sub =
map((id, dose, rate) -> Subject(; id, events = ev(dose, rate)), ids, dose, rate_ind)Population
Subjects: 3
Observations: 8 Simulation
Simulate the plasma concentration of the drug for all the subjects
Random.seed!(123)The random effects are zero’ed out since we are simulating a single subject
zfx = zero_randeffs(pk_41, pop3_sub, param)3-element Vector{@NamedTuple{η::Vector{Float64}}}:
(η = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0],)
(η = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0],)
(η = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0],)time_values = 0.1:0.01:10
sim_pop3_sub = simobs(pk_41, pop3_sub, param, zfx, obstimes = time_values)Simulated population (Vector{<:Subject})
Simulated subjects: 3
Simulated variables: dv, cp9 Visualization
We will build a DataFrame to facilitate plotting
df_plot = DataFrame(sim_pop3_sub; include_events = false)layer =
data(df_plot) *
mapping(:time => "Time (hours)", :cp => "Concentration (μg/L)", color = :id => "Dose") *
visual(Lines; linewidth = 4)
draw(
layer;
figure = (; fontsize = 22),
axis = (;
xticks = 0:10,
yscale = log10,
ytickformat = i -> (@. string(round(i; digits = 1))),
),
legend = (; position = :bottom),
)layer =
data(unique(df_plot, [:id, :cl])) *
mapping(:id => nonnumeric => "Dose", :cl => "Cl (L/hr/kg)") *
visual(ScatterLines, linewidth = 4, markersize = 22)
draw(layer; axis = (; yticks = 0.8:0.2:1.8,), figure = (; fontsize = 22))10 Simulating a Population
par = (
tvvmax = 180.311,
tvkm = 79.8382,
tvvc = 1.80036,
Ω = Diagonal([0.0462, 0.0628, 0.0156]),
σ²_prop = 0.0234,
)
ids = 1:60
doses = repeat([310, 520, 780]; inner = 20)
rates = repeat([62, 104, 156]; inner = 20)
pop = map(ids, doses, rates) do id, dose, rate
events = DosageRegimen(dose; cmt = 1, time = 0, rate, route = NCA.IVInfusion)
return Subject(; id, events)
end
Random.seed!(1234)
sim_pop = simobs(pk_41, pop, par, obstimes = [0, 0.1, 2, 5, 6, 8, 10])
df_sim = select(DataFrame(sim_pop; include_events = false), [:id, :time, :cp, :cl])
CSV.write("pk_41.csv", df_sim)"pk_41.csv"