using Random
using Pumas
using PumasUtilities
using CairoMakie
using AlgebraOfGraphics
using DataFramesMeta
using CSV
using Dates
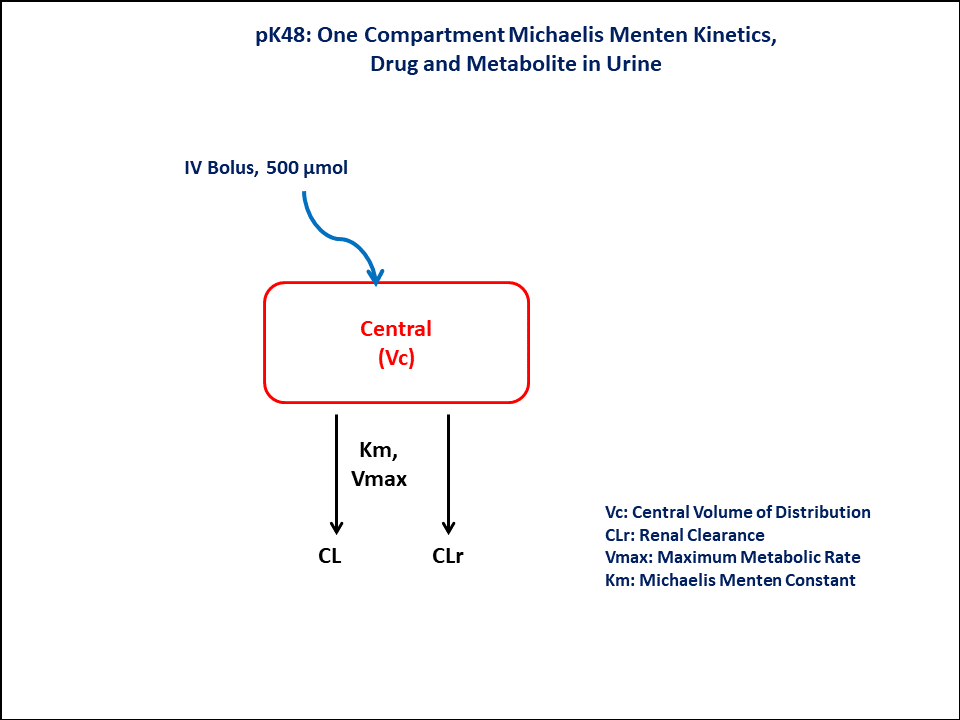
PK48 - One-compartment Michaelis-Menten kinetics - Drug and metabolite in urine
1 Background
- Structural model - One Compartment Michaelis Menten Kinetics, Drug and metabolite in Urine
- Route of administration - IV bolus
- Dosage Regimen - 500 μmol IV
- Number of Subjects - 1
2 Learning Outcome
In this model, you will learn
- To build a one compartment model for the drug given Intravenous Bolus dosage, following Michaelis Menten Kinetics.
- To apply differential equations in the model as per the compartment model.
3 Objectives
In this tutorial, you will learn how to build a one compartment Michaelis Menten Kinetics model, with drug and metabolite in urine.
4 Libraries
Call the necessary libraries to get started
5 Model
In this one compartment model, we administer the dose on the Central compartment.
pk_48 = @model begin
@metadata begin
desc = "One Compartment Michaelis Menten Kinetics Model"
timeu = u"hr"
end
@param begin
"""
Maximum rate of metabolism (μM/hr)
"""
tvvmax ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Michaelis Menten Constant (μM)
"""
tvkm ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Renal Clearance (L/hr)
"""
tvclr ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Central Volume of Distribution (L)
"""
tvvc ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
Ω ∈ PDiagDomain(4)
"""
Proportional RUV
"""
σ²_prop ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
end
@random begin
η ~ MvNormal(Ω)
end
@pre begin
Vmax = tvvmax * exp(η[1])
Km = tvkm * exp(η[2])
Clr = tvclr * exp(η[3])
Vc = tvvc * exp(η[4])
end
@vars begin
VMKM := Vmax * (Central / Vc) / (Km + (Central / Vc))
end
@dynamics begin
Central' = -VMKM - (Clr / Vc) * Central
UrineP' = (Clr / Vc) * Central
UrineM' = VMKM
end
@derived begin
cp = @. Central / Vc
ae_p = @. UrineP
ae_m = @. UrineM
"""
Observed Concentration (μmol/L)
"""
dv ~ ProportionalNormal.(cp, sqrt(σ²_prop))
"""
Observed Amount (μmol)
"""
dv_aep ~ ProportionalNormal.(ae_p, sqrt(σ²_prop))
"""
Observed Amount (μmol)
"""
dv_aem ~ ProportionalNormal.(ae_m, sqrt(σ²_prop))
end
end┌ Warning: Variable `cp` is defined in the `@derived` block using `=` and hence `cp` is not used for model fitting but only returned when simulating: │ If `cp` is a random variable, it must be defined in the `@derived` block using `~`; │ if `cp` should be returned when simulating, it should be defined in the `@observed` block using `=`; │ if `cp` is an intermediate quantity that should not be returned when simulating, it should be defined using `:=`. └ @ Pumas ~/run/_work/PumasTutorials.jl/PumasTutorials.jl/custom_julia_depot/packages/Pumas/qxx5c/src/dsl/model_macro.jl:2351 ┌ Warning: Variable `ae_p` is defined in the `@derived` block using `=` and hence `ae_p` is not used for model fitting but only returned when simulating: │ If `ae_p` is a random variable, it must be defined in the `@derived` block using `~`; │ if `ae_p` should be returned when simulating, it should be defined in the `@observed` block using `=`; │ if `ae_p` is an intermediate quantity that should not be returned when simulating, it should be defined using `:=`. └ @ Pumas ~/run/_work/PumasTutorials.jl/PumasTutorials.jl/custom_julia_depot/packages/Pumas/qxx5c/src/dsl/model_macro.jl:2351 ┌ Warning: Variable `ae_m` is defined in the `@derived` block using `=` and hence `ae_m` is not used for model fitting but only returned when simulating: │ If `ae_m` is a random variable, it must be defined in the `@derived` block using `~`; │ if `ae_m` should be returned when simulating, it should be defined in the `@observed` block using `=`; │ if `ae_m` is an intermediate quantity that should not be returned when simulating, it should be defined using `:=`. └ @ Pumas ~/run/_work/PumasTutorials.jl/PumasTutorials.jl/custom_julia_depot/packages/Pumas/qxx5c/src/dsl/model_macro.jl:2351
PumasModel
Parameters: tvvmax, tvkm, tvclr, tvvc, Ω, σ²_prop
Random effects: η
Covariates:
Dynamical system variables: Central, UrineP, UrineM
Dynamical system type: Nonlinear ODE
Derived: cp, ae_p, ae_m, dv, dv_aep, dv_aem
Observed: cp, ae_p, ae_m, dv, dv_aep, dv_aem6 Parameters
The parameters are as given below. Note that tv represents the typical value for parameters.
Vmax- Maximum rate of metabolism (μM/hr)Km- Michaelis Menten Constant (μM)Clr- Renal Clearance (L/hr)Vc- Central Volume of Distribution (L)Ω- Between Subject Variabilityσ- Residual error
param = (;
tvvmax = 51.4061,
tvkm = 5.30997,
tvclr = 2.46764,
tvvc = 24.5279,
Ω = Diagonal([0.04, 0.04, 0.04, 0.04]),
σ²_prop = 0.02,
)7 Dosage Regimen
Intravenous bolus dosing of 500 μmol to a single subject at time=0.
ev1 = DosageRegimen(500, cmt = 1, time = 0)1×10 DataFrame
| Row | time | cmt | amt | evid | ii | addl | rate | duration | ss | route |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Int8 | Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Float64 | Int8 | NCA.Route | |
| 1 | 0.0 | 1 | 500.0 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | NullRoute |
sub1 = Subject(id = 1, events = ev1)Subject
ID: 1
Events: 18 Simulation
Let’s simulate for plasma concentration with the specific observation time points after the IV bolus dose. Since we are simulating only a single subject, we can zero out the random effects
zfx = zero_randeffs(pk_48, sub1, param)(η = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],)Random.seed!(123)sim_sub1 = simobs(pk_48, sub1, param, zfx, obstimes = 0.1:0.1:15)SimulatedObservations
Simulated variables: cp, ae_p, ae_m, dv, dv_aep, dv_aem
Time: 0.1:0.1:15.09 Visualization
df = @chain DataFrame(sim_sub1) begin
dropmissing!(:cp)
@rsubset :time ∈ [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15]
stack([:cp, :ae_p, :ae_m])
end
plt =
data(df) *
mapping(
:time => "Time (hrs)",
:value,
color = :variable =>
renamer([
"cp" => "Parent Plasma Concentration",
"ae_p" => "Parent Urine Amount",
"ae_m" => "Metabolite Urine Amount",
]) => "Variable",
) *
visual(ScatterLines; linewidth = 4, markersize = 12)
fig = Figure()
gridpos = fig[1, 1]
f = draw!(
gridpos,
plt,
axis = (;
yscale = log10,
ytickformat = i -> (@. string(round(i; digits = 1))),
xticks = 0:2:16,
ylabel = "PK48 Concentrations (μmol/L) & Amount (μmol)",
),
)
legend!(
gridpos,
f;
tellwidth = false,
halign = :right,
valign = :center,
margin = (10, 10, 10, 10),
)
fig10 Population simulation
par = (;
tvvmax = 51.4061,
tvkm = 5.30997,
tvclr = 2.46764,
tvvc = 24.5279,
Ω = Diagonal([0.0432, 0.0368, 0.0213, 0.0123]),
σ²_prop = 0.00140536,
)
ev1 = DosageRegimen(500, cmt = 1, time = 0)
pop = map(i -> Subject(id = i, events = ev1), 1:55)
Random.seed!(1234)
pop_sim = simobs(pk_48, pop, par, obstimes = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15])
sim_plot(pop_sim)
df_sim = DataFrame(pop_sim)
#CSV.write("pk_48.csv", df_sim)