using PumasUtilities
using Random
using Pumas
using CairoMakie
using AlgebraOfGraphics
using CSV
using DataFramesMeta
using Dates
PK53 - Linear antibody kinetics of a two compartment turnover model
1 Background
- Structural model - Two compartment model
- Route of administration - Intravenous infusion
- Dosage Regimen - 0.77, 7.7, 77, 257, and 771 μmol/kg dose given as an intravenous infusion
- Number of Subjects - 1 (Monkey)
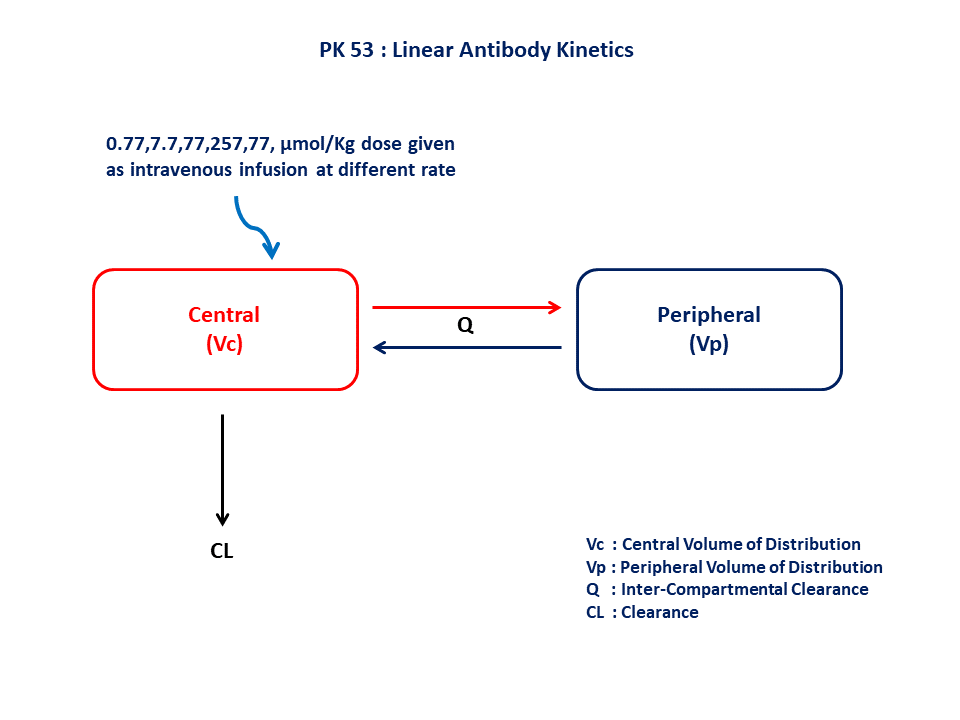
2 Learning Outcome
This exercise demonstrates simulating linear antibody kinetics of different doses of an IV infusion from a two compartment turnover model.
3 Objectives
To build a two-compartment turnover model to characterize linear antibody kinetics, simulate the model for a single subject given different IV dosage regimens, and subsequently perform a simulation for a population.
4 Libraries
Load the necessary libraries.
5 Model Definition
Note the expression of the model parameters with helpful comments. The model is expressed with differential equations. Residual variability is a proportional error model.
In this model, we administer the dose in the central compartment.
pk_53 = @model begin
@metadata begin
desc = "Two Compartment Model"
timeu = u"hr"
end
@param begin
"""
Volume of Central Compartment (L/kg)
"""
tvvc ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Volume of Peripheral Compartment (L/kg)
"""
tvvp ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Clearance (L/hr/kg)
"""
tvcl ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Intercompartmental CLearance (L/hr/kg)
"""
tvq ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
Ω ∈ PDiagDomain(4)
"""
Proportional RUV
"""
σ²_prop ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
end
@random begin
η ~ MvNormal(Ω)
end
@pre begin
Vc = tvvc * exp(η[1])
Vp = tvvp * exp(η[2])
CL = tvcl * exp(η[3])
Q = tvq * exp(η[4])
end
@dynamics begin
Central' = -(Q / Vc) * Central + (Q / Vp) * Peripheral - (CL / Vc) * Central
Peripheral' = (Q / Vc) * Central - (Q / Vp) * Peripheral
end
@derived begin
cp = @. Central / Vc
"""
Observed Concentration (μM)
"""
dv ~ ProportionalNormal.(cp, sqrt(σ²_prop))
end
end┌ Warning: Variable `cp` is defined in the `@derived` block using `=` and hence `cp` is not used for model fitting but only returned when simulating: │ If `cp` is a random variable, it must be defined in the `@derived` block using `~`; │ if `cp` should be returned when simulating, it should be defined in the `@observed` block using `=`; │ if `cp` is an intermediate quantity that should not be returned when simulating, it should be defined using `:=`. └ @ Pumas ~/run/_work/PumasTutorials.jl/PumasTutorials.jl/custom_julia_depot/packages/Pumas/qxx5c/src/dsl/model_macro.jl:2351
PumasModel
Parameters: tvvc, tvvp, tvcl, tvq, Ω, σ²_prop
Random effects: η
Covariates:
Dynamical system variables: Central, Peripheral
Dynamical system type: Matrix exponential
Derived: cp, dv
Observed: cp, dv6 Initial Estimates of Model Parameters
The model parameters for simulation are the following. Note that tv represents the typical value for parameters.
Cl- Clearance (L/hr/kg)Vc- Volume of Central Compartment (L/kg)Vp- Volume of Peripheral Compartment (L/kg)Q- Intercompartmental Clearance (L/hr/kg)Ω- Between Subject Variabilityσ- Residual error
param = (;
tvvc = 2.139,
tvvp = 1.5858,
tvcl = 0.00541,
tvq = 0.01640,
Ω = Diagonal([0.01, 0.01, 0.01, 0.01]),
σ²_prop = 0.04,
)7 Dosage Regimen
- Dose 1: 0.77 μmol/kg given as an IV-infusion at
time = 0 - Dose 2: 7.7 μmol/kg given as an IV-infusion at
time = 72.17 - Dose 3: 77 μmol/kg given as an IV-infusion at
time = 144.17 - Dose 4: 257 μmol/kg given as an IV-infusion at
time = 216.6 - Dose 5: 771 μmol/kg given as an IV-infusion at
time = 288.52
ev1 = DosageRegimen(0.77, time = 0, cmt = 1, duration = 0.416667)| Row | time | cmt | amt | evid | ii | addl | rate | duration | ss | route |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Int8 | Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Float64 | Int8 | NCA.Route | |
| 1 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.77 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 1.848 | 0.416667 | 0 | NullRoute |
ev2 = DosageRegimen(7.7, time = 72.17, cmt = 1, duration = 0.5)| Row | time | cmt | amt | evid | ii | addl | rate | duration | ss | route |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Int8 | Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Float64 | Int8 | NCA.Route | |
| 1 | 72.17 | 1 | 7.7 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 15.4 | 0.5 | 0 | NullRoute |
ev3 = DosageRegimen(77, time = 144.17, cmt = 1, duration = 0.5)| Row | time | cmt | amt | evid | ii | addl | rate | duration | ss | route |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Int8 | Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Float64 | Int8 | NCA.Route | |
| 1 | 144.17 | 1 | 77.0 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 154.0 | 0.5 | 0 | NullRoute |
ev4 = DosageRegimen(257, time = 216.6, cmt = 1, duration = 0.4)| Row | time | cmt | amt | evid | ii | addl | rate | duration | ss | route |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Int8 | Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Float64 | Int8 | NCA.Route | |
| 1 | 216.6 | 1 | 257.0 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 642.5 | 0.4 | 0 | NullRoute |
ev5 = DosageRegimen(771, time = 288.52, cmt = 1, duration = 0.5)| Row | time | cmt | amt | evid | ii | addl | rate | duration | ss | route |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Int8 | Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Float64 | Int8 | NCA.Route | |
| 1 | 288.52 | 1 | 771.0 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 1542.0 | 0.5 | 0 | NullRoute |
ev = DosageRegimen(ev1, ev2, ev3, ev4, ev5)| Row | time | cmt | amt | evid | ii | addl | rate | duration | ss | route |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Int8 | Float64 | Int64 | Float64 | Float64 | Int8 | NCA.Route | |
| 1 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.77 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 1.848 | 0.416667 | 0 | NullRoute |
| 2 | 72.17 | 1 | 7.7 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 15.4 | 0.5 | 0 | NullRoute |
| 3 | 144.17 | 1 | 77.0 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 154.0 | 0.5 | 0 | NullRoute |
| 4 | 216.6 | 1 | 257.0 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 642.5 | 0.4 | 0 | NullRoute |
| 5 | 288.52 | 1 | 771.0 | 1 | 0.0 | 0 | 1542.0 | 0.5 | 0 | NullRoute |
8 Single-individual that receives the defined dose
sub1 = Subject(id = 1, events = ev)Subject
ID: 1
Events: 59 Single-Subject Simulation
Simulate for plasma concentration with the specific observation time points after the intravenous administration.
Initialize the random number generator with a seed for reproducibility of the simulation.
Random.seed!(123)Define the timepoints at which concentration values will be simulated.
sim_sub1 = simobs(pk_53, sub1, param, obstimes = 0.01:0.01:2000)SimulatedObservations
Simulated variables: cp, dv
Time: 0.01:0.01:2000.0df1 = DataFrame(sim_sub1)
first(df1, 5)| Row | id | time | cp | dv | evid | amt | cmt | rate | duration | ss | ii | route | tad | dosenum | Central | Peripheral | η₁ | η₂ | η₃ | η₄ | Vc | Vp | CL | Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| String | Float64 | Float64? | Float64? | Int64? | Float64? | Symbol? | Float64? | Float64? | Int8? | Float64? | NCA.Route? | Float64? | Int64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | |
| 1 | 1 | 0.0 | missing | missing | 1 | 0.77 | Central | 1.848 | 0.416667 | 0 | 0.0 | NullRoute | 0.0 | 1 | missing | missing | -0.0645731 | -0.146325 | -0.16236 | -0.0217665 | 2.00524 | 1.36994 | 0.00459923 | 0.0160469 |
| 2 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.00921536 | 0.0101226 | 0 | 0.0 | missing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | missing | 0.01 | 1 | 0.018479 | 7.39373e-7 | -0.0645731 | -0.146325 | -0.16236 | -0.0217665 | 2.00524 | 1.36994 | 0.00459923 | 0.0160469 |
| 3 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.0184298 | 0.0220456 | 0 | 0.0 | missing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | missing | 0.02 | 1 | 0.0369562 | 2.95727e-6 | -0.0645731 | -0.146325 | -0.16236 | -0.0217665 | 2.00524 | 1.36994 | 0.00459923 | 0.0160469 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.0276432 | 0.0280853 | 0 | 0.0 | missing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | missing | 0.03 | 1 | 0.0554314 | 6.65338e-6 | -0.0645731 | -0.146325 | -0.16236 | -0.0217665 | 2.00524 | 1.36994 | 0.00459923 | 0.0160469 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.0368557 | 0.0482746 | 0 | 0.0 | missing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | missing | 0.04 | 1 | 0.0739047 | 1.18274e-5 | -0.0645731 | -0.146325 | -0.16236 | -0.0217665 | 2.00524 | 1.36994 | 0.00459923 | 0.0160469 |
10 Visualize Results
@chain DataFrame(sim_sub1) begin
dropmissing(:cp)
data(_) *
mapping(:time => "Time (hours)", :cp => "Concentration (μM)") *
visual(Lines; linewidth = 4)
draw(;
figure = (; fontsize = 22),
axis = (;
yscale = log10,
ytickformat = i -> (@. string(round(i; digits = 1))),
xticks = 0:200:2000,
),
)
end11 Population Simulation
We perform a population simulation with 48 participants, and simulate concentration values for 72 hours following 6 doses administered every 8 hours.
This code demonstrates how to write the simulated concentrations to a comma separated file (.csv).
par = (;
tvvc = 2.139,
tvvp = 1.5858,
tvcl = 0.0054,
tvq = 0.01653,
Ω = Diagonal([0.045, 0.024, 0.012, 0.0224]),
σ²_prop = 0.04,
)
ev = DosageRegimen(ev1, ev2, ev3, ev4, ev5)
pop = map(i -> Subject(id = i, events = ev), 1:50)
Random.seed!(1234)
sim_pop = simobs(
pk_53,
pop,
par,
obstimes = [
72.67,
74.17,
78.17,
84.17,
96.17,
120.17,
144.17,
144.67,
146.17,
150.17,
156.17,
168.17,
192.17,
216.17,
217,
218.5,
222.5,
228.5,
240.5,
264.5,
288.5,
289.02,
290.5,
294.5,
300.5,
312.5,
336.5,
360.5,
483.92,
651.25,
983.92,
1751.92,
],
)
pkdata_53_sim = DataFrame(sim_pop)
#CSV.write("pk_53_sim.csv", pkdata_53_sim)12 Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to build a two compartment turnover model to characterize linear antibody kinetics and perform a single subject and a population simulation.