using PumasUtilities
using Random
using Pumas
using PumasUtilities
using CairoMakie
using AlgebraOfGraphics
using CSV
using DataFramesMeta
using Dates
PK19 - Two compartment with limited capacity metabolite model
1 Background
- Structural model - Two Compartment model with a Metabolite Compartment
- Route of administration - IV Bolus
- Dosage Regimen - 10 μmol/kg, 50 μmol/kg, 300 μmol/kg
- Number of Subjects - 3
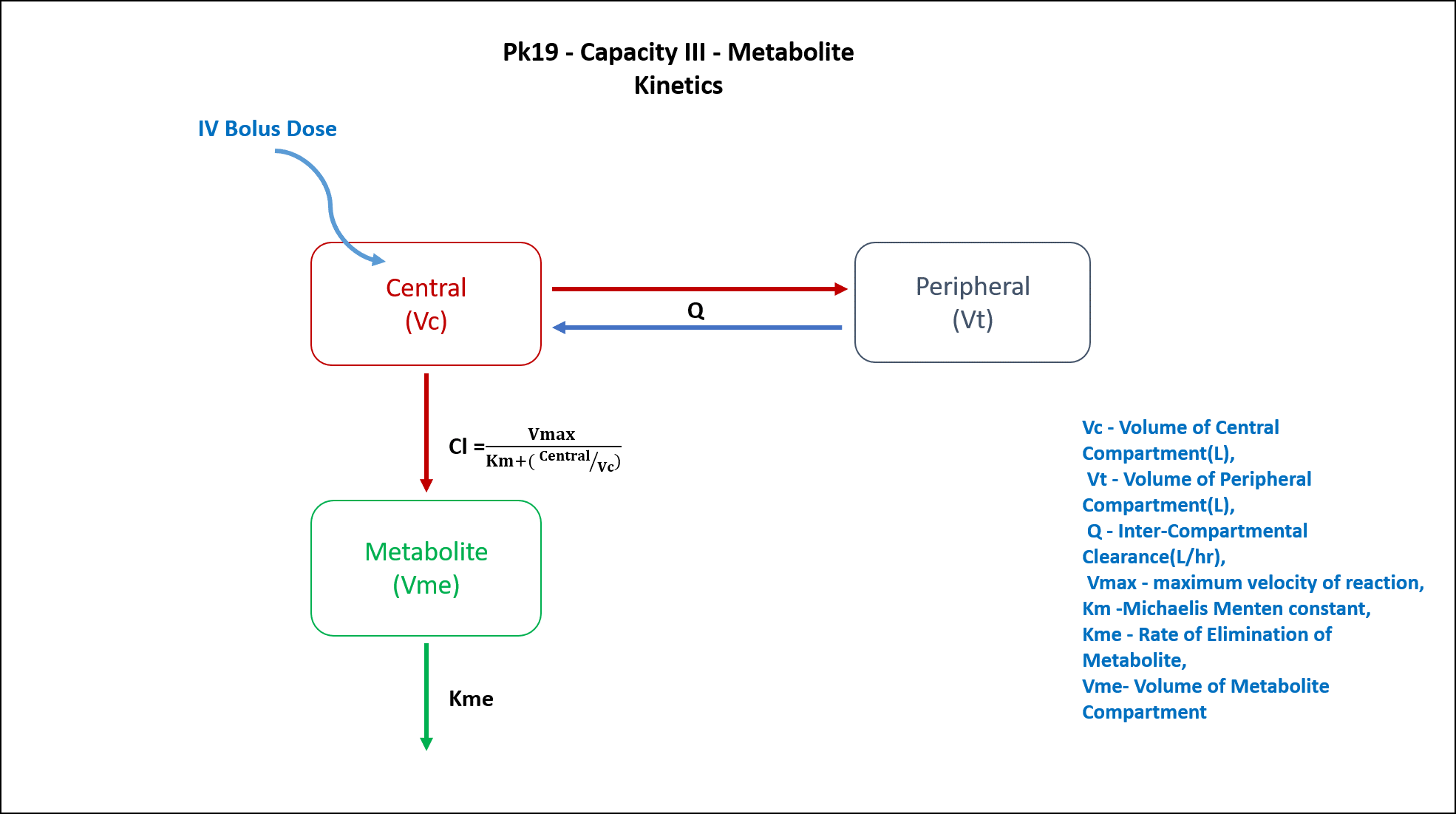
2 Learning Outcome
This exercise demonstrates simulating 3 different doses of a given IV bolus for 3 different subjects.
3 Objectives
To build a two-compartment model, simulate the model for subjects given 3 different IV doses of a drug undergoing capacity limited metabolite kinetics, and subsequently perform simulation for a population.
4 Libraries
Load the necessary libraries.
5 Model definition
Note the expression of the model parameters with helpful comments. The model is expressed with differential equations. Residual variability is a proportional error model.
In this two compartment model, we administer 3 different doses in 3 different subjects of a drug that undergoes metabolite kinetics.
pk_19 = @model begin
@metadata begin
desc = "Non-linear formation of Metabolite Model"
timeu = u"hr"
end
@param begin
"""
Volume of Central Compartment (L/kg)
"""
tvvc ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Volume of Perpheral Compartment (L/kg)
"""
tvvp ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Inter-Compartmental Clearance (L/min)
"""
tvq ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Maximum Velocity of Reaction (μmol/min/kg)
"""
tvvmax ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Michaelis-Menten constant (μmol/L)
"""
tvkm ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Rate of Elimination of Metabolite (min⁻¹)
"""
tvkme ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Volume of Metabolite Compartment (L/kg)
"""
tvvme ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
#Ω ∈ PDiagDomain(7)
Ω_vc ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0.0001)
Ω_vp ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0.0001)
Ω_q ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0.0001)
Ω_vmax ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0.0001)
Ω_km ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0.0001)
Ω_kme ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0.0001)
Ω_vme ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0.0001)
"""
Proportional RUV - Plasma
"""
σ_prop_cp ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
"""
Proportional RUV - Metabolite
"""
σ_prop_met ∈ RealDomain(lower = 0)
end
@random begin
η_vc ~ Normal(0, sqrt(Ω_vc))
η_vp ~ Normal(0, sqrt(Ω_vp))
η_q ~ Normal(0, sqrt(Ω_q))
η_vmax ~ Normal(0, sqrt(Ω_vmax))
η_km ~ Normal(0, sqrt(Ω_km))
η_kme ~ Normal(0, sqrt(Ω_kme))
η_vme ~ Normal(0, sqrt(Ω_vme))
end
@pre begin
Vc = tvvc * exp(η_vc)
Vp = tvvp * exp(η_vp)
Q = tvq * exp(η_q)
Vmax = tvvmax * exp(η_vmax)
Km = tvkm * exp(η_km)
Kme = tvkme * exp(η_kme)
Vme = tvvme * exp(η_vme)
end
@vars begin
VMKM := Vmax / (Km + (Central / Vc))
end
@dynamics begin
Central' = -VMKM * (Central / Vc) - (Q / Vc) * Central + (Q / Vp) * Peripheral
Peripheral' = (Q / Vc) * Central - (Q / Vp) * Peripheral
Metabolite' = VMKM * (Central / Vc) - Kme * Metabolite
end
@derived begin
cp = @. Central / Vc
"""
Observed Plasma Concentration (μmol/L)
"""
dv_cp ~ @. Normal(cp, cp * σ_prop_cp)
met = @. Metabolite / Vme
"""
Observed Metabolite Concentration (μmol/L)
"""
dv_met ~ @. Normal(met, met * σ_prop_met)
end
endPumasModel
Parameters: tvvc, tvvp, tvq, tvvmax, tvkm, tvkme, tvvme, Ω_vc, Ω_vp, Ω_q, Ω_vmax, Ω_km, Ω_kme, Ω_vme, σ_prop_cp, σ_prop_met
Random effects: η_vc, η_vp, η_q, η_vmax, η_km, η_kme, η_vme
Covariates:
Dynamical system variables: Central, Peripheral, Metabolite
Dynamical system type: Nonlinear ODE
Derived: cp, dv_cp, met, dv_met
Observed: cp, dv_cp, met, dv_met6 Initial Estimates of Model Parameters
The model parameters for simulation are the following. Note that tv represents the typical value for parameters.
Vc- Volume of Central Compartment (L/kg)Vp- Volume of Peripheral Compartment (L/kg)Q- Inter-Compartmental Clearance (L/min)Vmax- Maximum Velocity of Reaction (μmol/min/kg)Km- Michaelis-Menten constant (μmol/L)Kme- Rate of Elimination of Metabolite (min⁻¹)Vme- Volume of Metabolite Compartment (L/kg)Ω- Between Subject Variabilityσ- Residual error
param = (
tvvc = 1.06405,
tvvp = 2.00748,
tvq = 0.128792,
tvvmax = 1.64429,
tvkm = 54.794,
tvkme = 0.145159,
tvvme = 0.290811,
Ω_vc = 0.01,
Ω_vp = 0.01,
Ω_q = 0.01,
Ω_vmax = 0.01,
Ω_km = 0.01,
Ω_kme = 0.01,
Ω_vme = 0.01,
σ_prop_cp = 0.12,
σ_prop_met = 0.12,
)7 Dosage Regimen
Three Subjects were administered three different doses of 10 μmol/kg, 50 μmol/kg and 300 μmol/kg.
dose = [10, 50, 300]8 Single-individual that receives the defined dose
ids = ["ID:1 Dose 10", "ID:2 Dose 50", "ID:3 Dose 300"]ev(x) = DosageRegimen(dose[x], cmt = 1, time = 0)pop = map(zip(1:3, ids)) do (i, id)
return Subject(id = id, events = ev(i), observations = (cp = nothing, met = nothing))
endPopulation
Subjects: 3
Observations: cp, met9 Single-Subject Simulation
Simulate the parent plasma concentration and metabolite plasma concentration.
Initialize the random number generator with a seed for reproducibility of the simulation.
Random.seed!(123)Define the timepoints at which concentration values will be simulated.
sim_pop3_sub = simobs(pk_19, pop, param, obstimes = 0.1:1:300)Simulated population (Vector{<:Subject})
Simulated subjects: 3
Simulated variables: cp, dv_cp, met, dv_met9.1 Visualize Results
df_plots = DataFrame(sim_pop3_sub)
first(df_plots, 5)| Row | id | time | cp | dv_cp | met | dv_met | evid | amt | cmt | rate | duration | ss | ii | route | η_vc_1 | η_vp_1 | η_q_1 | η_vmax_1 | η_km_1 | η_kme_1 | η_vme_1 | Central | Peripheral | Metabolite | Vc | Vp | Q | Vmax | Km | Kme | Vme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| String? | Float64 | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Int64? | Float64? | Symbol? | Float64? | Float64? | Int8? | Float64? | NCA.Route? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | |
| 1 | ID:1 Dose 10 | 0.0 | missing | missing | missing | missing | 1 | 10.0 | Central | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | NullRoute | 0.107097 | -0.0429068 | -0.0207674 | 0.167946 | -0.0148676 | -0.0958827 | -0.0831824 | missing | missing | missing | 1.18433 | 1.92317 | 0.126145 | 1.94499 | 53.9854 | 0.131887 | 0.267599 |
| 2 | ID:1 Dose 10 | 0.1 | 8.33244 | 8.42832 | 0.0970993 | 0.0851387 | 0 | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | 0.107097 | -0.0429068 | -0.0207674 | 0.167946 | -0.0148676 | -0.0958827 | -0.0831824 | 9.86838 | 0.105461 | 0.0259837 | 1.18433 | 1.92317 | 0.126145 | 1.94499 | 53.9854 | 0.131887 | 0.267599 |
| 3 | ID:1 Dose 10 | 1.1 | 7.32551 | 9.75397 | 0.944867 | 0.785869 | 0 | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | 0.107097 | -0.0429068 | -0.0207674 | 0.167946 | -0.0148676 | -0.0958827 | -0.0831824 | 8.67584 | 1.05213 | 0.252846 | 1.18433 | 1.92317 | 0.126145 | 1.94499 | 53.9854 | 0.131887 | 0.267599 |
| 4 | ID:1 Dose 10 | 2.1 | 6.48584 | 7.60742 | 1.5981 | 1.39125 | 0 | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | 0.107097 | -0.0429068 | -0.0207674 | 0.167946 | -0.0148676 | -0.0958827 | -0.0831824 | 7.68139 | 1.82638 | 0.427652 | 1.18433 | 1.92317 | 0.126145 | 1.94499 | 53.9854 | 0.131887 | 0.267599 |
| 5 | ID:1 Dose 10 | 3.1 | 5.78536 | 5.69873 | 2.09364 | 2.05735 | 0 | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | missing | 0.107097 | -0.0429068 | -0.0207674 | 0.167946 | -0.0148676 | -0.0958827 | -0.0831824 | 6.85179 | 2.45781 | 0.560258 | 1.18433 | 1.92317 | 0.126145 | 1.94499 | 53.9854 | 0.131887 | 0.267599 |
9.2 Parent
@chain df_plots begin
dropmissing(:cp)
data(_) *
mapping(
:time => "Time (minutes)",
:cp => "Parent concentrations (μmol/L)";
color = :id => "",
) *
visual(Lines; linewidth = 4)
draw(
figure = (; fontsize = 22),
axis = (;
yscale = log10,
yticks = map(i -> 10.0^i, -1:2),
ytickformat = i -> (@. string(round(i; digits = 1))),
xticks = 0:50:300,
),
legend = (; position = :bottom),
)
end9.3 Metabolite
@chain df_plots begin
dropmissing(:met)
data(_) *
mapping(
:time => "Time (minutes)",
:met => "Metabolite concentrations (μmol/L)";
color = :id => "",
) *
visual(Lines; linewidth = 4)
draw(
figure = (; fontsize = 22),
axis = (;
yscale = log10,
yticks = map(i -> 10.0^i, -1:2),
ytickformat = i -> (@. string(round(i; digits = 1))),
xticks = 0:50:300,
),
legend = (; position = :bottom),
)
end10 Population Simulation
We perform a population simulation with 50 participants.
This code demonstrates how to write the simulated concentrations to a comma separated file (.csv).
par = (
tvvc = 1.06405,
tvvp = 2.00748,
tvq = 0.128792,
tvvmax = 1.64429,
tvkm = 54.794,
tvkme = 0.145159,
tvvme = 0.290811,
Ω_vc = 0.042,
Ω_vp = 0.0125,
Ω_q = 0.0924,
Ω_vmax = 0.0625,
Ω_km = 0.0358,
Ω_kme = 0.0111,
Ω_vme = 0.0498,
σ_prop_cp = 0.04587,
σ_prop_met = 0.0625,
)
ev1 = DosageRegimen(10, cmt = 1, time = 0)
pop1 = map(i -> Subject(id = i, events = ev1), 1:20)
ev2 = DosageRegimen(50, cmt = 1, time = 0)
pop2 = map(i -> Subject(id = i, events = ev2), 21:40)
ev3 = DosageRegimen(300, cmt = 1, time = 0)
pop3 = map(i -> Subject(id = i, events = ev3), 41:60)
pop = [pop1; pop2; pop3]
Random.seed!(1234)
pop_sim = simobs(pk_19, pop, par, obstimes = [0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 60, 90, 120, 180, 300])
sim_plot(pop_sim)
pkdata_19_sim = DataFrame(pop_sim)
#CSV.write("pk_19_sim.csv", pkdata_19_sim);11 Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to build a two-compartment model with a limited capacity metabolite of a given IV bolus and perform a single subject and population simulation.